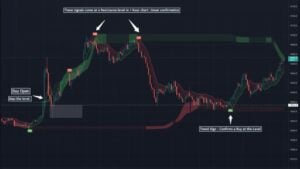
Overtrading occurs when traders make excessive trades, often driven by emotional or impulsive decisions rather than a well-thought-out strategy. This behavior can lead to increased transaction costs and reduced overall performance due to poor decision-making.
If you’re still on the fence, here are a few symptoms and signs of overtrading:
- High Trading Volume with Low Returns: Traders who overtrade often make many trades with minimal or negative returns due to increased transaction costs and suboptimal trading decisions.
- Increased Trading Activity Without Proper Analysis: Traders frequently entering and exiting positions without thorough analysis or a clear strategy are likely overtrading.
- Emotional Trading: Making trades based on emotions like fear or greed rather than a disciplined approach can signify overtrading.
- Frequent Monitoring of Positions: Constantly watching the market and adjusting positions can indicate an overactive trading behavior.
Stop Overtrading Decisively – Tips From An Experienced Trader
1. Develop a Solid Trading Plan
Set Clear Entry and Exit Points:
Identify specific conditions under which you will enter a trade. This could involve using indicators like moving averages, support and resistance levels, or other technical signals to back your decisions.
Determine in advance when you will exit a trade. This includes setting stop-loss levels to limit potential losses and take-profit levels to lock in gains. Tools like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) to identify overbought or oversold conditions can help decide when to exit a trade.
Pro Tip: Always use stop-loss orders. They act as a safety net, preventing significant losses if the market moves against you.
Risk Management Strategies:
Here are some key risk management techniques:
- Position Sizing: Determine the size of your trades based on your overall trading capital and risk tolerance. A common rule of thumb is to risk no more than 1-2% of your total trading capital on a single trade.
- Stop-Loss Orders: As mentioned earlier, stop-loss orders are essential. They help you cut losses and prevent emotional decision-making.
- Take-Profit Orders: These orders help you lock in profits at predefined levels. Setting take-profit levels ensures that you secure gains before the market reverses.
Advice: Use a risk-reward ratio of at least 1:2. For every dollar you risk, you aim to make two dollars in profit.
2. Maintain Trading Discipline
Avoid Impulsive Trades:
Impulsive trading, driven by emotions like FOMO or greed, often leads to overtrading. Maintaining discipline is key to successful trading.
- Stick to Your Plan: Once you have a trading plan, stick to it. Avoid making trades based on hunches or market noise. Only enter trades that meet your predefined criteria.
- Trading Journal: Keeping a trading journal can help you track and review your trades. Documenting each trade, including the reasons for entering and exiting, helps you stay disciplined and learn from past mistakes.
Automate Trading Strategies:
Automation can help eliminate the emotional aspect of trading and ensure consistency.
- Automated Trading Systems: Use automated trading systems or bots that execute trades based on predefined criteria. These systems can be programmed to follow your trading plan precisely.
Platforms like TradingView offer automated trading features. You can set specific conditions for entering and exiting trades, and the system will execute them automatically.
- Backtesting: Backtest your strategy using historical data before implementing an automated system. This helps you understand how your strategy would have performed in the past and make necessary adjustments.
3. Limit the Number of Trades
Focus on Quality Over Quantity:
Prioritize trades with a higher probability of success based on your analysis. Wait for setups that meet all your criteria rather than jumping into every opportunity.
Advice: Set a maximum number of trades per day or week. For example, limit yourself to three trades per day to avoid overtrading.
Implement Time Constraints:
Define specific hours during which you will trade. This can help you avoid constantly monitoring the market and making impulsive trades.
Tip: Focus on trading during high-liquidity periods, such as the opening hours of major stock exchanges. These periods often provide better trading opportunities.
4. Educate Yourself Continuously
Learn from Past Mistakes: Regularly review your trades to identify patterns, mistakes, and areas for improvement. Analyze both successful and unsuccessful trades to understand what worked and what didn’t.
Stay Updated with Market Trends:
Stay informed about economic indicators, market news, and trends. Understanding the broader market context can help you make better trading decisions.
5. Seek Professional Help if Needed
Seeking guidance from experienced traders can significantly improve your skills and discipline.
Mentorship: Consider finding a mentor who can provide personalized guidance and help you refine your trading strategy.
Trading Courses: Enroll in trading courses to learn new strategies and techniques. Many online platforms offer comprehensive courses for traders of all levels.
You can always join us as we help you trade smarter. Both our **free and premium dashboards at Zeiierman** include several courses, strategies and learning opportunities.
6. Join a Trading Community
Engage with other traders to share experiences, strategies, and tips. Being part of a community can provide motivation and help you stay committed to your trading plan.
Zeiierman Trading Community
Our Discord channel provides a platform for traders to connect, share ideas, and receive mentorship from experienced traders. Engaging with a supportive community can help you stay disciplined and focused on your trading goals.
Case Study: Who Trades Profusely? By Daniel Richards and Gizelle D. Willows
“Who Trades Profusely? The Characteristics of Frequent Trading Individual Investors” is a research paper published by Daniel Richards and Gizelle D. Willows
The paper highlights that frequent trading harms investor performance. Research by Barber and Odean (2000) shows that investors who trade excessively earn lower returns due to higher transaction costs and the bid-ask spread.
Characteristics of Frequent Traders:
- Demographic Factors: Younger and male investors are more likely to trade frequently. The study found that younger investors and males are more prone to overconfidence, which drives them to trade more often.
- Medium of Trade: Internet and telephone investors tend to trade more frequently. The ease of access provided by online trading platforms can lead to more impulsive trading decisions.
The data revealed a positively skewed distribution in trading frequency among investors. Specifically, the top 10% of the most frequently traded investors completed 50.1% of the total trades, accounting for 53.48% of the total value.
In contrast, the 0-80th percentile of investors, who traded the least, completed only 32.79% of the total number of trades and 31% of the total value.
Suggested Strategies to Reduce Overtrading:
- Buy and Hold Strategy: Long-term investing helps minimize transaction costs and capitalizes on the market’s natural growth over time.
- Limiting Trading Platforms: The study suggests that simplifying the trading process can help reduce impulsive trading decisions.
- Focus on Risk Management: Implementing proper risk management strategies, such as setting realistic stop-loss levels and avoiding emotional reactions to market movements, can help mitigate overtrading.
Consequences of Overtrading

1. Financial Impacts
Increased Transaction Costs: Overtrading leads to higher transaction costs, including broker fees, spreads, and slippage. These costs will quickly erode profits.
If you make 50 trades a month with an average commission of $10 per trade, you incur $500 in transaction costs.
Lower Returns: Frequent trading without a clear strategy often results in lower returns. Overtrading can lead to poor entry and exit points, reducing the overall profitability of trades.
Increased Risk Exposure: Overtrading can lead to over-leveraging and higher exposure to market risk. This increased exposure can result in significant losses, particularly in volatile markets.
2. Psychological Impacts
Stress and Anxiety: Constant monitoring of the market and frequent trading can lead to high-stress levels and anxiety. This emotional strain can affect decision-making and lead to further trading mistakes.
Burnout: Overtrading can lead to burnout, where traders feel exhausted and lose motivation. This burnout can impact not only trading performance but also overall well-being.
3. Performance Impacts
Poor Decision-Making: The pressure to constantly be active in the market can lead to impulsive and poorly thought-out decisions. This behavior undermines the effectiveness of any trading strategy.
Lack of Consistency: Overtrading often results in a lack of consistency in trading performance. Without a disciplined approach, traders may experience significant fluctuations in their returns.