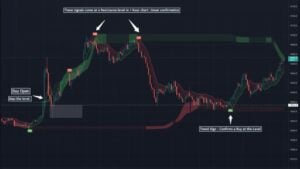
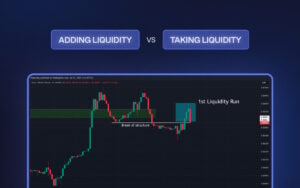
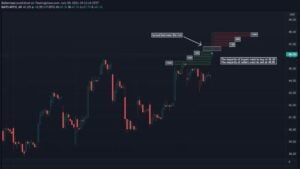
Investors use iceberg orders to hide their true intentions in the market. They hide the true size of a trade order by breaking it into smaller pieces. Basically, iceberg order allows traders to buy or sell large amounts of a security without significantly affecting the price.
Institutional investors and high-frequency traders often use iceberg orders to minimize market impact and maximize profits.
An iceberg order typically comprises a large parent order and several smaller child orders. The parent order is the total size of the order, while the child orders are smaller pieces of the parent order.
The child orders are placed at different prices and times, and the parent order is not visible to the market.
1. How do Iceberg Orders help with trading?
An iceberg order is divided into two parts: the visible portion and the hidden portion. The visible portion is the amount of the order that is displayed on the order book. The hidden portion is the amount of the order that is not displayed in the order book.
When an iceberg order is placed, the visible portion of the order is executed first. Once the visible portion is filled, the hidden portion of the order is executed.
Using an iceberg order, you can buy or sell large amounts of securities without worrying about the market price being affected.
Example:
Imagine you own a large investment firm and want to purchase 100,000 shares of Apple. Instead of placing a single order for the entire quantity, which could lead to a sudden spike in demand and impact the stock price, you’ll use an iceberg order.
So, even if the parent order is 100,000 shares, only 5,000 are visible on the order book anytime. As these visible shares get executed, new hidden portions become visible, allowing you to gradually accumulate the desired quantity without alarming the market.
Iceberg orders can also be used to hide the identity of the trader. It’s especially beneficial for traders who want to remain anonymous.
2. Pros and Cons of Iceberg Orders in Trading

Iceberg orders can be beneficial in certain situations, but they also have some drawbacks that should be considered before using them.
Pros:
The primary benefit of using an iceberg order is that it allows traders to buy or sell large amounts of securities without alarming the market. And you get to remain anonymous.
Another benefit is that it can help traders avoid the risk of slippage. Slippage occurs when the price of a security moves against the trader before the entire order is filled. You can reduce the risk of slippage by breaking up the order into smaller pieces.
Cons:
However, there are also some drawbacks to using iceberg orders.
One of the primary drawbacks is that it can be difficult to execute the order promptly. Since the order is broken up into smaller pieces, it can take longer to fill the entire order. It’s especially problematic in fast-moving markets where prices can change quickly.
In addition, iceberg orders can also be more expensive to execute than traditional orders. Since the order is broken up into smaller pieces, the trader may have to pay more in commissions and fees.
3. How to Use Iceberg Orders to Maximize Profits in Trading?
Step one is to determine the order size. It should be based on the amount of capital available and the desired level of risk. Once you have the size, divide the entire order into smaller orders and get ready to place them on the market.
Step two is to determine the timing of the orders. The timing of the orders should be based on the market conditions and the desired level of risk.
For example, if the market is volatile, the orders should be placed at different times to reduce the risk of slippage. If the market is stable, the orders can be placed simultaneously.
Step three is to monitor the orders to ensure they are executed at the desired price. If the orders are not executed at the desired price, adjust or cancel them. Trust your gut.
Finally, monitor the profits. You have to ensure that the desired profit level is achieved. If the profits are not meeting the desired level, adjust or cancel the orders and reevaluate your positions.
4. Strategies for Managing Risk with Iceberg Orders in Trading
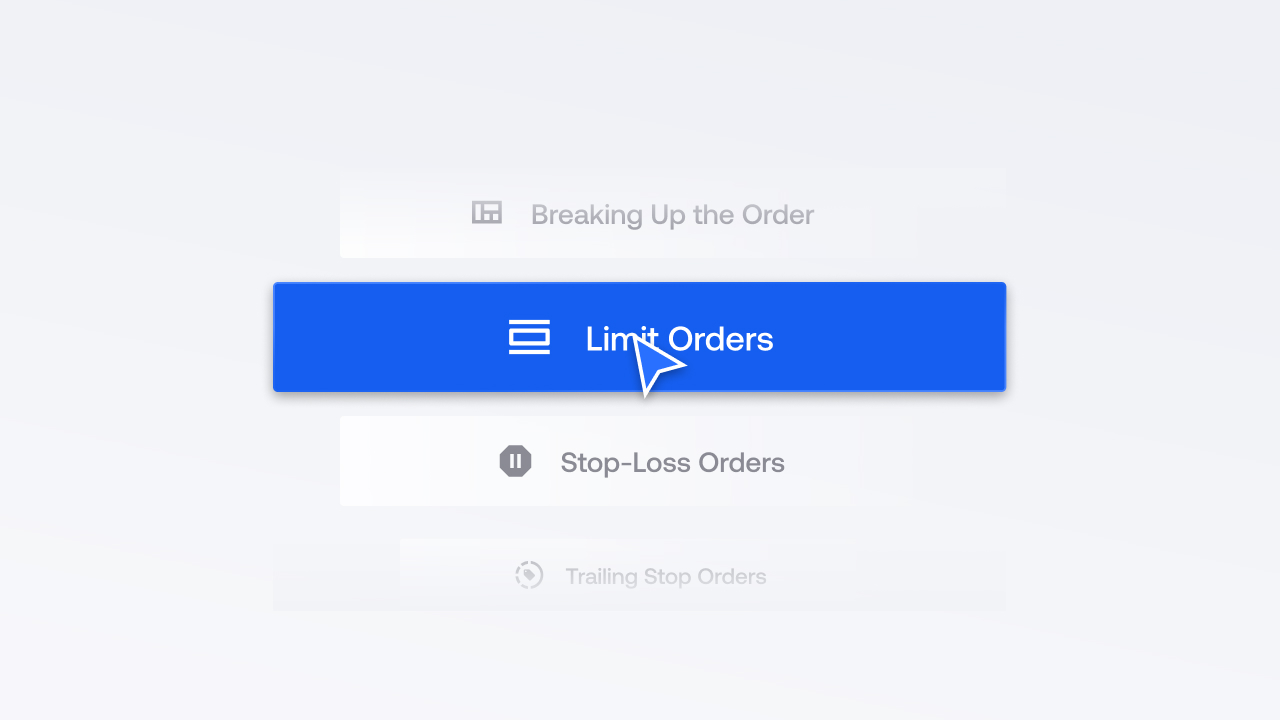
In trading, managing risks associated with iceberg orders is crucial for successful execution. Here are key strategies for effective risk management:
a. Breaking Up the Order:
One fundamental strategy is breaking up the order into smaller pieces. By dividing a large order, traders can spread their impact over time, minimizing disruptions to the market. This strategy is particularly useful in volatile markets where sudden price movements are more likely.
b. Limit Orders:
Utilizing limit orders is another essential risk management technique. Traders can set the maximum price they are willing to buy or sell a stock. It protects them against unexpected price movements that may occur due to the execution of the iceberg order.
c. Stop-Loss Orders:
Implementing stop-loss orders is crucial for limiting potential losses. Traders can set a predetermined price at which they automatically sell a stock if it drops below a certain level, providing a safety net in case of adverse market movements.
d. Trailing Stop Orders:
Trailing stop orders are dynamic and adjust with market conditions. Traders set a price to automatically sell a stock if it drops below a certain level. This strategy helps lock in profits and protect against sudden price drops associated with iceberg orders.
5. Examining the Impact of Iceberg Orders on Market Volatility

Iceberg orders have been controversial, as some argue that they can be used to manipulate the market. Proponents, however, argue that they can be used to reduce market volatility, as they allow traders to enter and exit the market without making large, visible trades.
Researchers have conducted several studies to examine the impact of iceberg orders on market volatility. These studies have generally found that iceberg orders reduce market volatility, although the magnitude of the effect varies depending on the type of order and the market conditions.
For example, one study found that iceberg orders reduced volatility in the S&P 500 index by approximately 0.2%. Another study found that the effect was more pronounced in the NASDAQ, where iceberg orders reduced volatility by 0.5%.
Overall, the evidence suggests that iceberg orders can reduce market volatility, although the magnitude of the effect varies depending on the type of order and the market conditions. As such, traders must consider the potential impact of iceberg orders when making trading decisions.
6. Conclusion
Iceberg orders are a powerful tool for traders who want to buy or sell large amounts of stock without moving the market.
They allow traders to break up large orders into smaller pieces and execute them over time, reducing the risk of market impact. Iceberg orders can reduce market impact, increase liquidity, and reduce transaction costs. They are an important tool for traders who want to trade large amounts of stock without moving the market.